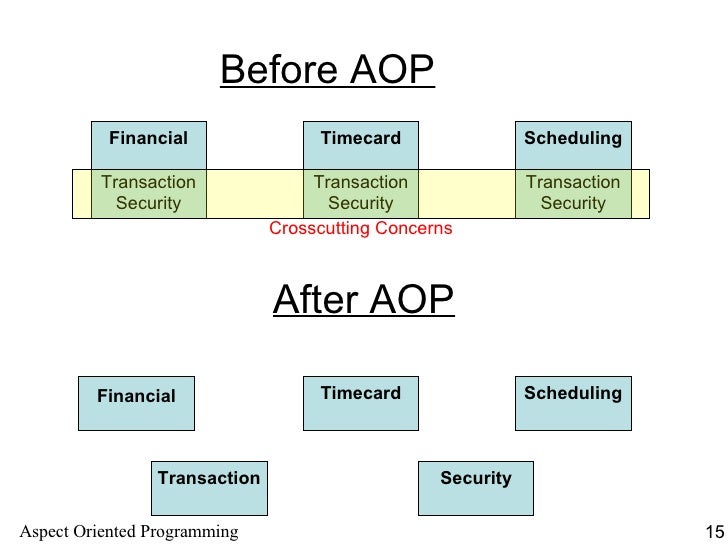
Attribute-oriented programming (@OP) is a technique for embedding metadata, namely attributes, within program code.
Attribute-oriented programming in various languages
Java
With the inclusion of Metadata Facility for Java (JSR-175) into the J2SE 5.0 release it is possible to utilize attribute-oriented programming right out of the box. XDoclet library makes it possible to use attribute-oriented programming approach in earlier versions of Java.
C#
The C# language has supported attributes from its very first release. These attributes was used to give run-time information and are not used by a preprocessor. Currently with source generators, you can use attributes to drive generation of additional code at compile-time.
UML
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) supports a kind of attribute called stereotypes.
Hack
The Hack programming language supports attributes. Attributes can be attached to various program entities, and information about those attributes can be retrieved at run-time via reflection.
Tools
- Annotation Processing Tool (apt)
- Spoon, an Annotation-Driven Java Program Transformer
- XDoclet, a Javadoc-Driven Program Generator
References
External links
- Don Schwarz. Peeking Inside the Box: Attribute-Oriented Programming with Java5
- Sun JSR 175
- Attributes and Reflection - sample chapter from Programming C# book
- Modeling Turnpike Project
- Fraclet Archived 2008-09-20 at the Wayback Machine: An annotation-based programming model for the Fractal component model
- Attribute Enabled Software Development book